views
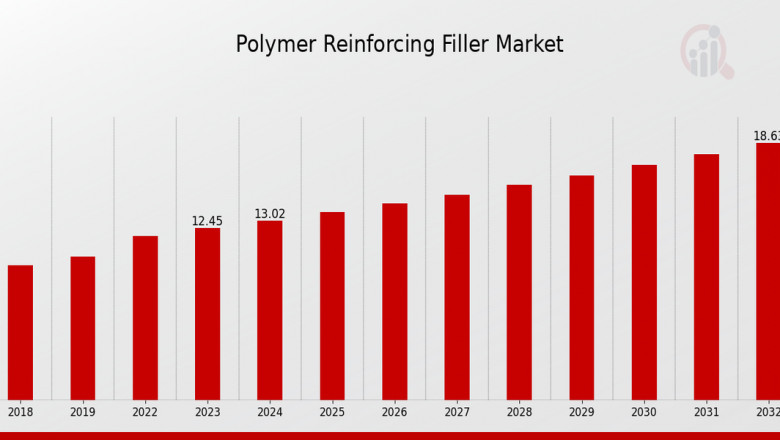
In the fast-evolving world of material science, polymer reinforcing fillers are quietly revolutionizing industries ranging from automotive to construction and consumer electronics. As the demand for stronger, lighter, and more durable materials increases, the Polymer Reinforcing Filler Market is expanding in both value and innovation. This article takes a fresh look at this market, highlighting the emerging trends, novel applications, and future growth drivers.
What Are Polymer Reinforcing Fillers?
Polymer reinforcing fillers are materials added to polymers (plastics, elastomers, or resins) to enhance mechanical strength, stiffness, impact resistance, and sometimes even thermal and electrical conductivity. Common fillers include:
- Carbon black – for strength and conductivity
- Glass fibers – for stiffness and heat resistance
- Silica and silicates – for abrasion resistance
- Nanoclays and carbon nanotubes – for next-gen reinforcement with lightweight profiles
These fillers interact with polymer matrices to create composites that offer performance far beyond what base materials can achieve on their own.
Why the Market Is Booming
Several macro trends are fueling the growth of the polymer reinforcing filler market:
- Lightweighting in Automotive & Aerospace
Fuel efficiency and emission norms are pushing automakers and aircraft manufacturers toward lighter materials. Reinforced polymers offer a sweet spot: low weight, high strength, and moldability. As electric vehicles (EVs) go mainstream, demand for lightweight, thermally stable components is surging.
- Sustainability Pressure
As industries pivot to green solutions, there's growing interest in bio-based and recycled fillers like natural fibers (hemp, jute, flax), cellulose, and agricultural byproducts. These offer performance boosts while reducing the carbon footprint.
- Construction & Infrastructure Boom
The use of reinforced polymer composites in construction is rising due to their corrosion resistance, design flexibility, and longevity. Applications range from reinforced pipes and panels to geotextiles and concrete modifiers.
Emerging Trends in the Market
▶️ Nano-fillers Gaining Traction
Nanotechnology is making fillers smarter. Graphene, carbon nanotubes, and nano-silica are enabling next-gen composites with better barrier properties, conductivity, and strength—even at low loadings.
▶️ Functional Fillers for Smart Materials
Fillers are no longer just about strength. Emerging types offer flame retardancy, antimicrobial action, EMI shielding, or self-healing properties—making polymers more versatile across industries.
▶️ 3D Printing Compatible Fillers
The additive manufacturing industry is hungry for reinforced filaments. Fillers like chopped carbon fiber and mineral particulates are being tailored for FDM, SLA, and SLS processes, expanding design and performance boundaries.
Challenges in the Market
Despite its growth, the market faces challenges:
- Dispersibility Issues: Ensuring even distribution of fillers at the micro- or nanoscale without agglomeration is a technical hurdle.
- Cost vs. Benefit: Advanced fillers like carbon nanotubes or graphene come at a premium. Manufacturers must balance cost with performance.
- Compatibility with Bioplastics: As biopolymer use grows, ensuring filler compatibility with new eco-resins remains a research focus.













Comments
0 comment